Prostatitis is a common disease that can affect men of any age. It is an inflammatory disease of the prostate gland that causes various symptoms and has negative consequences for men's health. In this article, we will review the causes, symptoms, and treatment methods of prostatitis, as well as discuss preventive measures to protect men's health.
Definition of disease. Causes of the disease
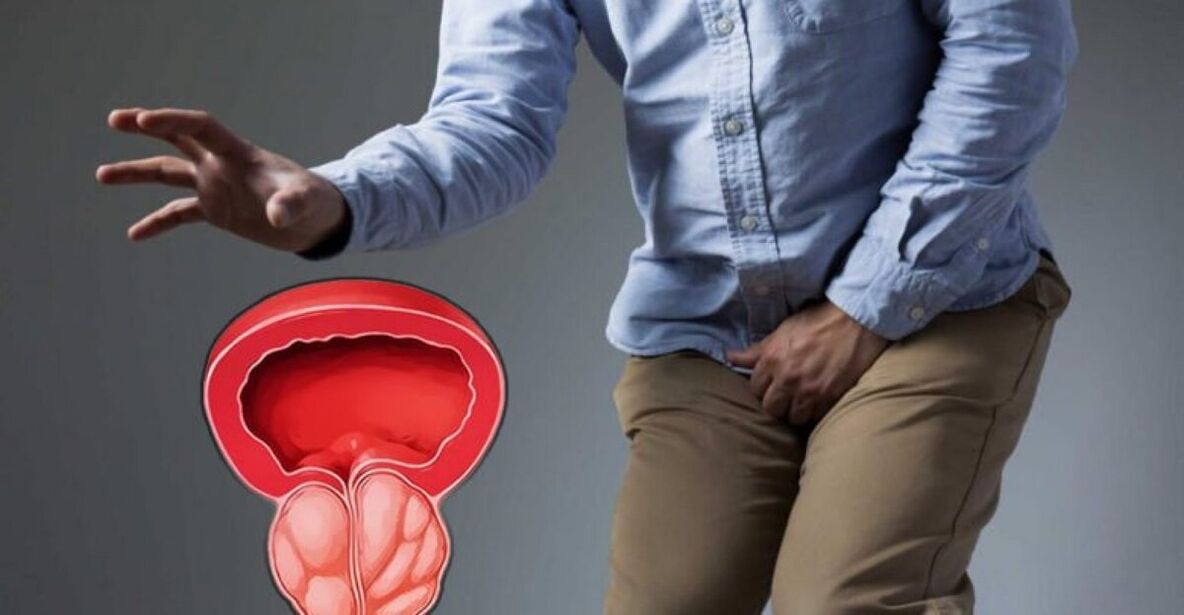
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland in men, causing various symptoms and difficulty urinating.
Prostatitis can be caused by various causes such as infections, injuries, allergies and stress. Some of the most common causes of prostatitis include:
- Bacterial infection: This is the most common cause of prostatitis. Bacteria can enter the prostate gland through the urinary tract or blood, causing inflammation.
- Chronic constipation: Long-term constipation can put stress on the prostate gland, which can lead to inflammation.
- Sexual problems: Prolonged lack of sexual activity or sexual fatigue can lead to the development of prostatitis.
- Autoimmune diseases: Some autoimmune diseases can cause inflammation of the prostate gland.
- Damage to the prostate gland: Damage to the prostate gland can cause inflammation.
- Irregular sexual activity: Lack of regular sexual activity can lead to stagnation of secretions in the prostate gland, which can lead to inflammation.
Knowing the causes of prostatitis will help prevent its development. To prevent the development of prostatitis, it is necessary to monitor your health and consult a doctor at the first signs of the disease.
Symptoms of prostatitis
Prostatitis can manifest itself with various symptoms that are unpleasant and have a negative impact on the quality of life of men. Some of the most common symptoms of prostatitis include:
- Pain and discomfort in the perineum, rectum or bladder.
- Painful urination, sometimes with a burning sensation or pain.
- The need to urinate more often than usual, including at night.
- Weak, intermittent, or difficult urination.
- Sexual problems, such as pain or discomfort during erection or ejaculation.
- Feeling tired or generally weak.
- Increased body temperature and fever.
- Increased sensitivity to cold.
- Pain with pressure on the prostate.
- The appearance of blood in the urine or semen.
Symptoms of prostatitis can be different and appear at different times and with different degrees of severity. If you suspect prostatitis, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Pathogenesis of prostatitis
The pathogenesis of prostatitis includes a complex of changes occurring in the prostate gland and other tissues of the male body during the inflammatory process.
Bacterial prostatitis develops when bacteria enter the prostate gland through the genitourinary system or blood. The inflammatory process leads to the expansion of capillaries and damage to the walls of blood vessels, which causes swelling of tissues and disruption of blood microcirculation. In addition, bacteria can continue to multiply and produce toxins, which contribute to inflammation.
Non-infectious non-bacterial prostatitis can be caused by various factors, such as chronic stress, autoimmune diseases, allergies, microcirculation disorders, etc. In non-bacterial prostatitis, there is no obvious infection, but some scientists associate it with changes in the function of the nervous system and disturbances in the immune system.
The general mechanism of prostatitis pathogenesis includes disruption of the normal microflora of the prostate gland, inflammatory response, tissue damage and prostate gland dysfunction. The most effective approach to the treatment of prostatitis is complex treatment, including antibacterial therapy, painkillers, physiotherapeutic procedures, prostate massage and other methods of influence. Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor!
Classification and stages of development of prostatitis
There are several classifications of prostatitis, but the most common causes are based on:
- Bacterial prostatitis caused by a bacterial infection.
- Chronic prostatitis/Chronic postprostatitis syndrome is characterized by persistent symptoms, but no inflammatory process is detected.
- Chronic abacterial prostatitis caused by non-infectious causes.
- Acute prostatitis is characterized by a rapid onset of the disease, severe pain and severe symptoms.
The stages of development of prostatitis can be different, but generally there are three:
- Acute prostatitis. Early onset of the disease, pain, burning during urination, fever, etc. Acute prostatitis can be caused by a bacterial infection and requires immediate treatment.
- Chronic prostatitis/Chronic postprostatitis syndrome. Symptoms are always present and can last for months or even years. There may be no inflammatory process and the symptoms may be non-infectious in nature.
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis. Symptoms are constantly present, but the inflammatory process is not detected. This type of prostatitis can be caused by various reasons, such as stress, prolonged constipation, microcirculation disorders, etc.
Knowing the classification and development stages of prostatitis can help in timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease. If you notice the symptoms of prostatitis, you should consult a doctor for further diagnosis and treatment.
Complications of prostatitis
Prostatitis can cause various complications that can negatively affect men's health. Some of the more common complications of prostatitis include:
- Prostate cancer.
- Epididymitis is an inflammation of the testicle.
- Sclerosing lymphangitis.
- Seminal cyst.
- Sepsis.
- Dysfunction of the prostate gland.
- Increased risk of developing depression and other psychological problems.
It should be remembered that prostatitis is a serious disease that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. If you suspect prostatitis, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
Diagnosis of prostatitis includes a physical examination, urine and blood tests, and other additional tests.
During a physical exam, your doctor will examine the prostate gland through the rectum to assess its size, shape, and texture. If the prostate gland is enlarged or has an abnormal shape, it may indicate the presence of prostatitis.
A urine test will detect the presence of bacteria and other indicators of inflammation. Signs of inflammation will also appear in the blood.
Additional tests may include prostate ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, biopsy, and other methods.
Your doctor may also recommend a prostate antigen (PSA) test. This substance is produced by the prostate gland and can be elevated during prostatitis, prostate cancer and other diseases.
In general, the diagnosis of prostatitis can be difficult because the symptoms of prostatitis can be very similar to the symptoms of other genitourinary diseases. Therefore, if you suspect prostatitis, it is important to see a doctor for professional diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment of prostatitis
Treatment of prostatitis depends on the type and cause of the disease. Bacterial prostatitis is treated with antibiotics aimed at killing the bacteria that cause the infection.
In the case of chronic prostatitis/chronic postprostatitis syndrome, if no infection is found, a combination of drugs may be used, including antibiotics, anti-inflammatories and diuretics, as well as drugs that improve blood flow to the prostate gland.
Chronic abacterial prostatitis is treated with drugs, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs that improve blood circulation in the prostate gland, and drugs that improve urination.
Additional treatment for prostatitis includes physical therapy, prostate massage, and lifestyle changes such as proper nutrition, exercise, adequate rest, and stress management.
It should be remembered that the treatment of prostatitis is prescribed only by a qualified doctor. If you suspect prostatitis, see a urologist or andrologist for diagnosis and treatment.
Forecast. Prevention
The prognosis of prostatitis depends on the type and degree of the disease. Bacterial prostatitis can be successfully treated if treatment is started on time. Chronic prostatitis can cause long-term discomfort, but is usually not a life-threatening condition.
Prevention of prostatitis includes:
- Maintaining hygiene means washing the genitals regularly and using a condom during sex.
- Avoid hypothermia - clothing should be appropriate for the weather and avoid sitting on cold surfaces.
- Avoiding smoking and alcohol.
- Eat right and drink enough water.
- Regular medical examination to detect diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Regular exercise and stress management.
It is important to know that prostatitis is a serious disease that can negatively affect a man's quality of life. Therefore, at the first signs of the disease, it is important to consult a doctor for preventive medical examinations and timely treatment.
The modern clinic is suitable for professional diagnosis and treatment. The clinic will offer you a comprehensive diagnosis, including a medical examination, blood and urine tests, ultrasound and other additional studies.
Depending on the diagnostic results, the clinic's specialists can prescribe individual treatment, including drugs, physiotherapy, prostate massage, lifestyle changes and other treatment methods.
In addition, at the clinic, you can receive advice from qualified specialists and recommendations on the prevention of prostatitis and other diseases of the genitourinary system.
If you suspect prostatitis, do not delay to consult a doctor. A professional clinic will help to identify and treat the disease as soon as possible.